Fast, fully automated MRI-based measurement of the human corpus callosum
Timothy J Herron (US Veterans Affairs, Neurology), Xiaojian Kang (UC Davis, Neurology & Neuroscience), And U Turken (US Veterans Affairs Research), David L Woods (US Veterans Affairs & UC Davis)
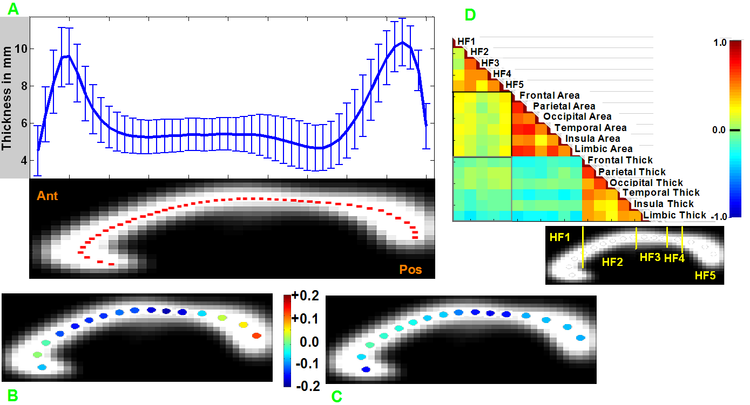
We present a stand-alone open-source MatLab software package, C8, which measures midsagittal cross-sectional thickness and area of the human corpus callosum from high-resolution T1 in vivo MR images. C8 quickly extracts and measures the callosum using segmented, affine normalized brains as input. Areas are computed for geometrically defined callosal compartments according to several different extant compartment schemes. Thickness is sampled along a median line within the callosum according to three methods of spacing the samples: equal angle, equal-distance, and equal-area. Coregistered accessory input images have values sampled along the median line and near the edges of the callosum. The algorithm’s performance was tested using the high-quality OASIS image database [www.oasis-brains.org] and showed C8 producing consistent, reliable callosal measurement estimates over repeated scans and with values comparable to manually-segmented callosa.
We used 1000+ medium quality T1 images from the 1000 Functional Connectomes Project [fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org] to evaluate between group differences in measured callosum values and regional effects of age and gender on thickness measures. We also sampled normalized T1 values along the callosum to capture regional variation.

 Latest news for Neuroinformatics 2011
Latest news for Neuroinformatics 2011 Follow INCF on Twitter
Follow INCF on Twitter